We are now living in a digital era! Where almost all our tasks are been handle to a sophisticated machine called computer for processing. When we want to listen a song, we used digital media player, for shopping we used internet service, for communication and sharing of information, we also used digital devices that have internet access. In our offices and homes, we used computer to run our tasks, etc.
As we may already know, a computer is an electronic device that can accept data, stores the data in memory, process the data and brings out the results of the processed data as an information to the computer user or send to the other devices attached to the computer in electronic form.
Computers are made up of two (2) basic constituents, namely;
- Computer Hardware, and
- Computer software
Computer software are the instructions/commands that tells computer what to do, how to perform actions, and when to execute a command. The software part of a computer controls all the hardware components of the computer. It’s like a soul of our computing machine that makes it to breaths and control all the body parts of the computer. You can read more about the computer software by clicking here!
All the physical components of a computer is what we called a hardware. Hardware are the physical components of a computer that we can see, handle, or carry around. The hardware components are classified according to the service they provide such as input, memory, storage, processing, output, power management, etc.
In this article, we’re going to talk on the basics hardware that have to presence on the computer before we can be able to use the device. These basics hardware includes the monitor, keyboard, mouse etc.
The complete computer set up that was used to perform any operation is basically consists of a monitor, keyboard, mouse, the system unit/case, and power cord. Each part of these plays an important role whenever you use a computer. One can also attach accessories if needed, such as printers and scanners by means of ports. Increasingly in the workplace, computers are connected to printers and other computers by means of a network.
THE MONITORS
The Monitor is the Visual Display Unit (VDU). The monitor looks like a television screen and is where you see what is happening on your computer. The Monitor display images and texts by using shadows and graphics with over a million different colours, much of what you see will appear 3-dimensional. The monitor works with a video card, located inside the computer case on the motherboard, to display images and text on the screen.
Newer monitors usually have LCD (liquid crystal display) or LED (light-emitting diode) displays. These can be made very thin, and they are often called flat-panel displays. Older monitors use CRT (cathode ray tube) displays. CRT monitors are much larger and heavier, and they take up more desk space.

Computer monitor
Image credit: Image by OpenClipart-Vectors from Pixabay
Monitors come in different sizes. The size of the monitor is measured diagonally on the screen in inches. Based on this, the monitors range in sizes of 12", 14", 15", 17", 19", 21", 29" etc.
THE SYSTEM CASE/UNIT
The computer case often called system unit/case is the metal and plastic box that contains the main components of the computer, including the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), memory chips (RAM), and power supply. The front of the case usually has an On/Off button, casing USB ports, Webcams, and one or more optical drives.
Computer cases come in different shapes and sizes. A desktop case lies flat on a desk, and the monitor usually sits on top of it. A tower case is tall and sits next to the monitor or on the floor. All-in-one, such as Apple desktop computers came with the internal components built into the monitor, which eliminates the need for a separate case. This component on the computer case, looks very different in desktops and laptops, but it works the same.
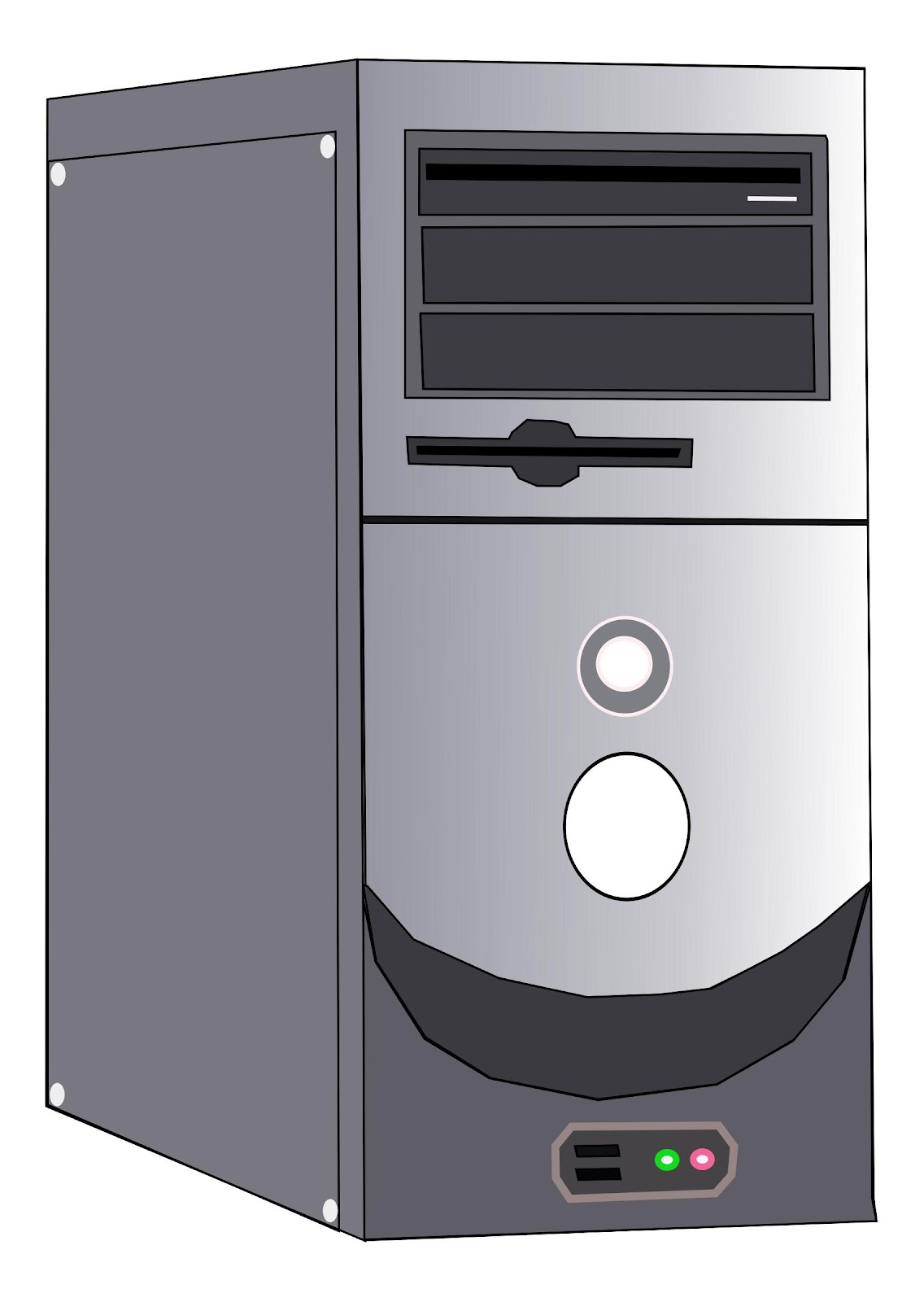
Desktop Computer system case/unit

Apple iMac All-in-one Computer
COMPUTER KEYBOARD
The keyboard is the basic input device. It is one of the ways you can tell the computer what to do. There are many different types of keyboards, but most are very similar and allows you to accomplish the same basic tasks. The keyboard is made of three main categories of keys with each used for a different purpose.
- Character Keys: These comprise of letters, numbers and the symbols. They are used to insert/display readable characters on the screen which is equivalent to the keystroke pressed.
- Action Keys: These are not used to type anything, instead they cause an action. It includes the Escape, Tab, Caps Lock, Shift, Control, Alt, Backspace, Enter, Windows, Print Screen, Scroll Lock, Pause Break, Number Lock, Insert, Home, Page Up, Delete, End, Page Down, Up Arrow, Left Arrow, Right Arrow, Down Arrow, and Space Bar keys.
- Application-Dependant Keys: These are called function keys. They are F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8, F9, F10, F11, and F12 keys.
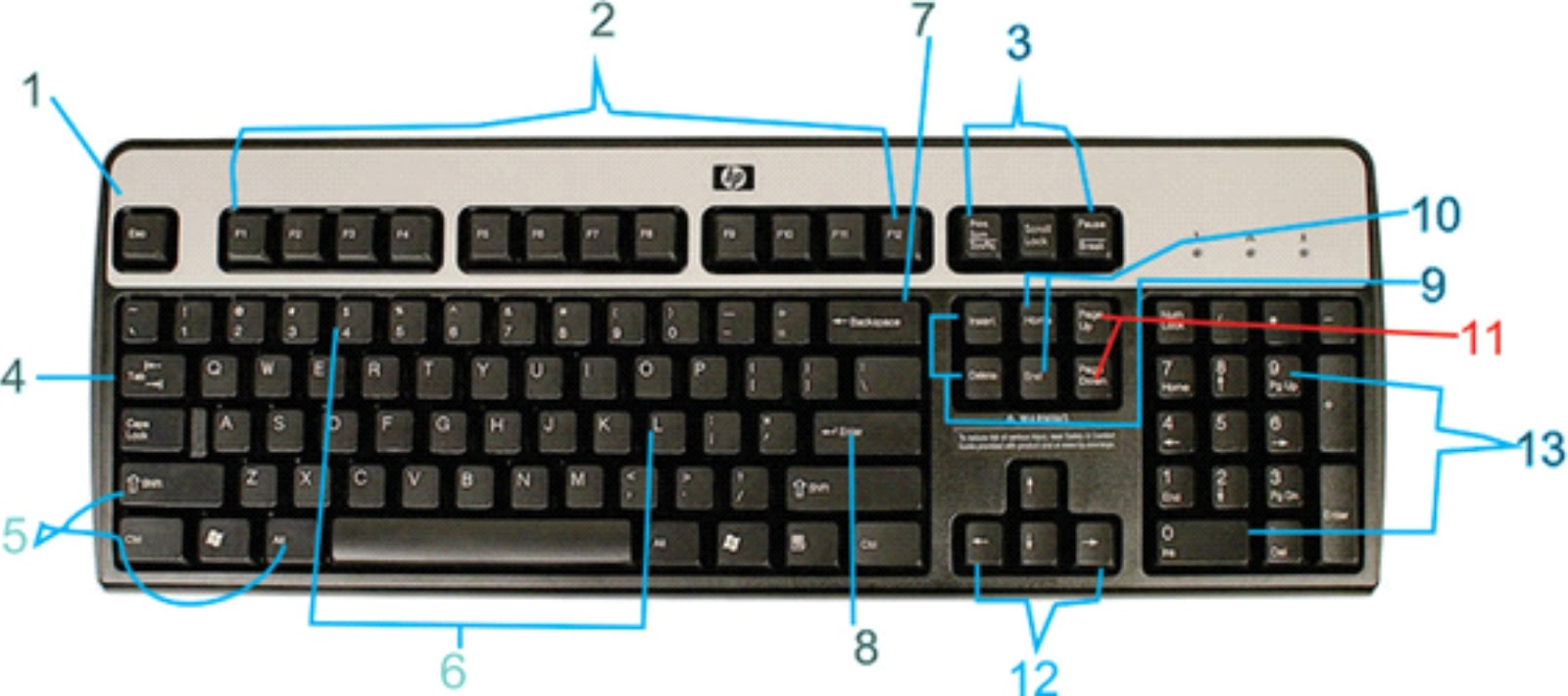
Computer Keyboard
The table below, explain the functions of each parts of the Computer keyboard.
| NO. | Part of the Keyboard | Function(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Escape Key | The Escape (Esc) key allows you to stop a function or action. For example, if a webpage is taking a long time to load, you can press the Escape key to stop loading it. |
| 2 | Function Keys | The function keys are labelled F1 through F12. Some programs use these keys as shortcuts for common tasks. For example, in many programs, F1 opens the Help file. |
| 3 | Print Screen, Scroll Lock, Pause/Break | The Print Screen, Scroll Lock, and Pause/Break keys are at the top-right corner of the keyboard. The Print Screen key takes a picture of your screen (called a screenshot) that you can edit or save using a graphics program. Scroll Lock and Pause/Break are rarely used today, so some keyboards don't have them |
| 4 | Tab Key | The Tab key is used to create indents in word processing programs. Also, if you are filling out a form online, you can use the Tab key to switch to the next field. |
| 5 | Ctrl, Alt, and Shift | The Control (Ctrl), Alternate (Alt), and Shift keys are designed to work in combination with other keys. Typically, you hold down Ctrl, Alt, or Shift and then type another key to perform a specific task. For example, in many programs, typing Ctrl+S will save a file. |
| 6 | Alphanumeric Keys | The main part of the keyboard includes the alphanumeric keys (letters and numbers) and the spacebar |
| 7 | Backspace key | The Backspace key erases the character to the left of the cursor. |
| 8 | Enter Key | The Enter key executes commands. For example, while on the Internet, you can type a website address and then press Enter to go to the site. It is also used to start a new line in word processing programs. |
| 9 | Insert and Delete | Insert, this switches between insert mode (which inserts new text without deleting anything) and overtype mode (which deletes text after the cursor as you type). Delete, this erases the character to the right of the cursor. |
| 10 | Home and End | These move the cursor to the beginning or end of the current line. |
| 11 | Page Up and Page Down | These scroll a document or webpage up or down |
| 12 | Arrow keys | The arrow keys are used for many different purposes, including moving the cursor, scrolling a document, and controlling a game. |
| 13 | Numeric Keypad | The numeric keypad resembles a calculator keypad. Many users find that it is easier to type numbers using this keypad. On some keyboards, these keys double as arrow keys. |
Different Parts of a Computer Keyboard with their functions
Tips for Using Keyboard:
- When typing, you only have to quickly press the key to make it appear on the screen. If you hold it down too long, multiple same letters will appear, such as by pressing and holding down the key "r" will result in something like - rrrrrr.
- When the caps locks is activated, a light appears on the keyboard
- When typing, remember to press on the space bar after typing each word in a sentence. If you forget, your sentences will appear as one long word.
MOUSE/TOUCHPAD
The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. Commonly known as a pointing device It lets you point to objects on the screen, click on them, and move them. Most mice (Mouse - singular) have two buttons — a right and a left button — and a scrolling wheel. Mice come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Some of the strangest looking mice often look that way because they are designed to be more ergonomic than traditional mice. There are other devices that can do the same thing as a mouse, known as a Trackball/Touchpad.
Pressing the LEFT mouse button is called “left-clicking,” while pressing the RIGHT mouse button is called “right-clicking”. Left-clicking is used far more often than right clicking.

Computer Mouse
Image credit: Image by Clker-Free-Vector-Images from Pixabay
Operating a Mouse: Left-Clicking, Double-Clicking and Right-Clicking
One of the most difficult things to learn when first beginning to use a computer, is how to use the mouse. It takes coordination, precision, and patience. Fortunately, the more you practice, the easier it will become The mouse symbol, or pointer, that appears on the computer screen will change its look and function depending on what it is near or hovering over, such as:
- Your mouse pointer will most often look like an arrow.
- When your mouse pointer is over an internet link, it will look like a pointing hand
- When your mouse pointer is over a place where you can type, it will look like an I-beam
- When your computer is busy or ‘working,’ your mouse pointer may look like an hourglass or a spinning circle.
There are actually many different pointers (though these are the most common), and they will change automatically depending on what task you are trying to perform. The buttons on the mouse may also have different functions, depending on which program you are using. If you are working in Microsoft Word, for example, the mouse will offer options related to Microsoft Word. Conversely, if you are working in Photoshop Graphic program, the mouse will offer options related to Photoshop Graphic program, and so on. For now, remember these rules:
- The LEFT mouse button SELECTS items.
- The RIGHT mouse button GIVES YOU MORE OPTIONS.
- Double-Clicking the LEFT mouse button EXECUTES options (for example, you can open a program by double-clicking an icon on the desktop).
- Double-Clicking the RIGHT mouse button does not do anything.
Techniques for Using Mouse
The mouse can be used in many different ways. Some of the most used mouse techniques include:
- Click: This is the easiest of the techniques, however it is very important that you do it properly. To click, you press down one of the mouse buttons. As you click it, it makes a “clicking” noise. The most important skill to learn when clicking is that it only takes a very light, short tap to click a mouse button. Don’t click the mouse too hard since this tends to slow you down. Once you have mastered clicking, you will be ready to move on to the next most essential practice, pointing.
- Left Clicking: This is the primary “click” that you will use. This is clicking on the left mouse button. When someone says, “click here,” that usually means to do a left click.
- Right Clicking: This is used to change options or perform specific functions.
- Point: Use the mouse to move the mouse pointer so that it hovers over the top of an icon or word on the screen. Sometimes, this is all that you need to do in order to prompt a response from the computer (as an example, the shape of your cursor may change).
- Point and click: Move the mouse pointer over the top of an item (such as an icon) on your screen and then (while holding your hand still) gently press and release the left button on the mouse. This technique is often used to make a selection.
- Double-click: While hovering the mouse pointer over an item on the screen, quickly press the left mouse button two times. This may take some practice but it is a very useful and important skill. If you are having problems double clicking, it’s most likely because you’re moving the mouse slightly when double clicking. Try to steady your hand and try it again. By double clicking, you are usually prompting the computer to take an action on the item you selected (double clicking on an icon on your computer desktop may open or start a program).
- Click and drag: Press and hold down a mouse button (usually the left button). As you hold down the button, move the mouse in any direction. Click and drag is a method used when “highlighting” or “selecting” text. To do this to text, click at the beginning of the text that you want to select, hold down the left mouse button, and move your mouse to the end of where you want to highlight.
- The Right Mouse Button: It is mostly used to display a textual menu, where a set of commands will show-up.
Knowing fully the details operations of the hardware components of computer greatly assists us in handling and managing different devices on the computer machine.
Also, understanding the tips and concept on using the mouse and keyboard can go a very long way for us in handling and operating such components, which could also improve the ways we perform tasks on the computer.
 Bluehole Techs
Bluehole Techs

No comments:
Post a Comment