Article Contents
- Introduction
- Definition and Overview
- Cloud storage and computing
- How does cloud storage works
- Categories/Models of cloud computing
- Benefits and Challenges of cloud computing

Cloud Computing Technology
Introduction
One of the amazing things with internet is the ability for the users to be able to keep the data or files somewhere that is very far away from the user. You don’t need to have physical contact with the cloud computer and storage devices that stores your data. However, you can be able to work with all your data directly from the cloud computer on your device using the internet, remotely via web or other apps interface. All of these processes and storage capabilities that we can be able to carried out remotely over the internet is a terminology called Cloud Computing/Storage
Definition and Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a collection of networked computer hardware and software that works together to provide many aspects of computing in the form of an online services. It is also the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power such as the processor and RAM, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of computing hardware and software resources to the users; the term known as virtual computing.
Today, individuals can have access to several free cloud computing services available around the globe, such as Google drive, OneDrive, Dropbox and Amazon AWS, which allows you to harness the cloud storage capabilities for storing files and information remotely. This comes with upgraded subscription packages that offer larger storage sizes and additional cloud services. Also, there are hundreds of deployed cloud software services that we could used from any device that can connect to these services remotely.
One of the central features of the cloud computing is virtualisation. Virtual machines are created with software that subdivides the computing power, memory and storage of a given machine into multiple smaller units, each running their own operating system. This virtualisation allows computing resources to be shared and allocated efficiently across devices.
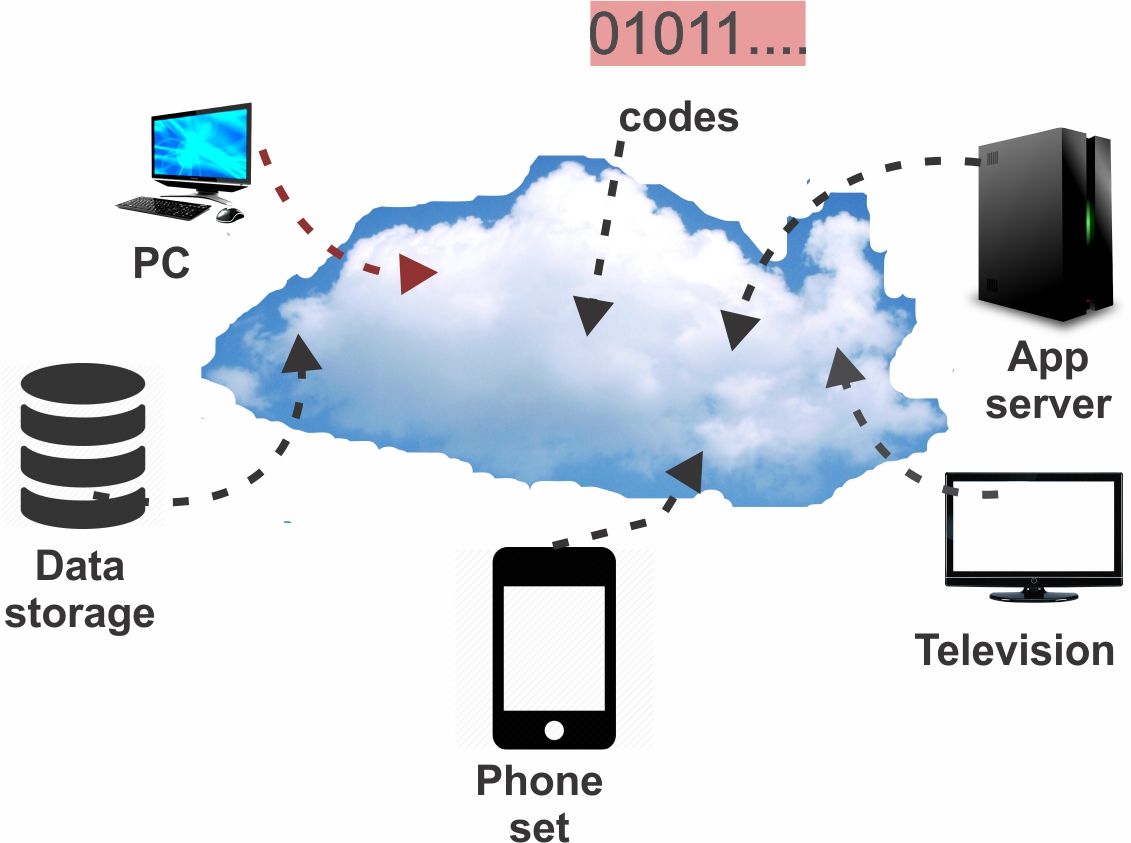
Cloud Computing service and Facilities
Cloud storage servers are virtual servers; software-defined servers that emulate physical servers. A physical server can host multiple virtual servers, making it easier to provide cloud-based storage solutions to multiple customers. The use of virtual servers increase efficiency because physical servers otherwise typically operate below capacity, which means some of their processing power is wasted.
Cloud Computing vs Cloud Storage
Cloud storage involves storing data on a hardware storage device in a remote physical location, which can be accessed from any device via the internet. Clients send files to a data server maintained by a cloud provider instead of storing it on their own disk drives. Google Drive, which allow users store and share files, is a good example of cloud storage. Cloud storage systems/server generally encompass hundreds of data servers linked together by a master control server, but the simplest system might involve just one data server.

Amazon cloud storage service Facilities
Cloud Computing on the other hand, involves clients connecting to remote computing infrastructure via a network, but this time, the infrastructure includes shared processing power such as the processor, main memory, software and other resources. This free users from having to constantly update and maintain their software and hardware systems, while at the same time allowing them to harness the processing power of a vast network. Familiar everyday services powered by cloud computing include social networks like Facebook, webmail clients like Gmail, online banking apps, and online image editing service such as pixlr.
How Does Cloud Storage Work?
In cloud computing, cloud storage services work as a network of connected data servers collectively used to share and access your files across devices. Cloud storage providers own and maintain the offsite servers that make up this network at their data centers. Users can upload files to the servers and access their files/information stored in the cloud via website, desktop app, or mobile app.
Cloud storage works by allowing a client computer, tablet, or smartphone to send and retrieve files online to and from a remote data server. The same data is usually stored on more than one server simultaneously so that clients can always access their data even if one server is down or loses data due to some disaster.
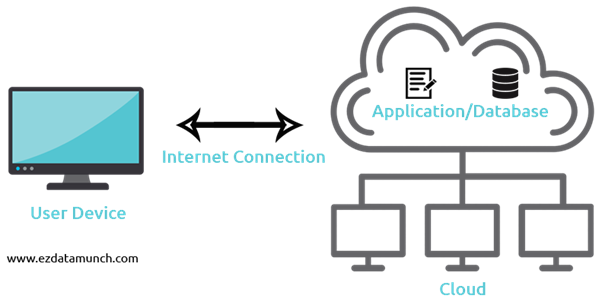
How Cloud Computing Work
A cloud storage system can specialize in storing a particular type of data such as digital photos or music files, or can be used to provide general storage of any type of data such as photos, audio files, text documents, presentations, spreadsheets etc.
Safety and Security of the Data in Cloud System
Data centres are owned and maintained by cloud service providers. Once you’ve put your data in the cloud, it may be physically stored in many different places, countries or even continents, depending on where the service provider’s data centres are located. The cloud may also promise to lift the burden of our ever-increasing data storage needs. But our main concerns are how do we know our data is truly safe when we entrust it to a cloud provider, and what measures do they take to address these two biggest fears; reliability and security?
We’ve already learned that cloud providers store backups of data at multiple locations. Also, systems that detect smoke, suppress fires and provide emergency power are also standard features of data centres, and these secret locations are heavily reinforced, guarded and internally protected to prevent intruders or disgruntled employees from physically harming or stealing the storage hardware.
To also secure the data so no one else can get at it, cloud systems use two basic methods: authentication processes like usernames and passwords to limit access to the data, and data encryption to protect data from been stolen or intercepted en-route. Though, passwords can be hacked, but often it’s the service provider who holds the encryption keys to your data.
Cloud storage companies always tried to maintain their reputation; they take great pains to employ the most advanced security techniques and provide the most reliable service possible.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud service models describe how cloud services are made available to clients. The most fundamental service models were categorized into three, which include infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). These service models may have synergies between each other and be interdependent; for example, PaaS is dependent on IaaS because application platforms require physical infrastructure.
- The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model provides infrastructure components to clients. Components may include virtual machines, computing resources, storage, networks, firewalls, load balancers, and so on. With IaaS, clients have direct access to the lowest-level software in the stack – that is, to the operating system on virtual machines, or to the management dashboard of a firewall or load balancer.
Examples of IaaS include Amazon EC2 and S3, Terremark Enterprise Cloud, Windows Live Skydrive and Rackspace Cloud. - Platform as a service (PaaS): Platform as a Service (PaaS) is another application delivery model. PaaS supplies all the resources required to build applications and services completely from the Internet, without having to download or install software. It allows customers to develop new applications using API deployed and configurable remotely. The platform model offers include development tools, configuration management, and deployment platforms. Application developers develop and run their software on a cloud platform instead of directly buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. With some PaaS, the underlying computer and storage resources scale automatically to match application demand so that the cloud user does not have to allocate resources manually. An example of PaaS is Google AppEngine and web CMS.
- SaaS (Software as a Service) is what traditionally comes to our mind when we think of cloud computing (if any part of cloud computing can be considered traditional). In SaaS, an application is hosted by a service provider and then accessed via the World Wide Web by a client. Cloud consumers release their applications on a hosting environment, which can be accessed through networks from various clients (e.g. web browser, PDA, etc.) by application users.
In the SaaS model, cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud clients. Cloud users do not manage the cloud infrastructure and platform where the application runs. This eliminates the need to install and run the application on the cloud user's own computers, which simplifies the maintenance and support.
Examples of applications offered as SaaS are games and productivity software like Google Docs, MS-Word Online, Pixlr, and so forth.
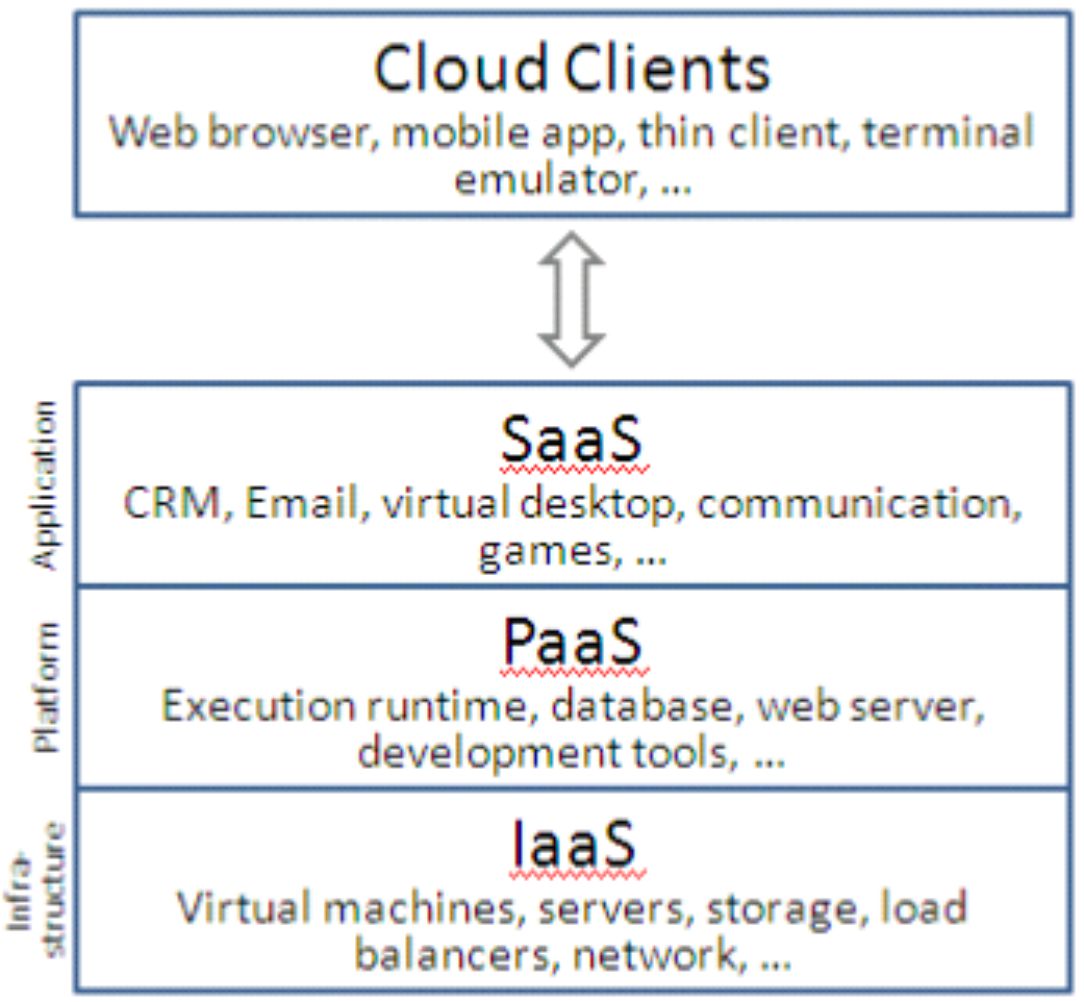
Cloud Computing Service Models
The main difference between SaaS and PaaS is that SaaS only hosts completed cloud applications, whereas PaaS offers a development platform that hosts both completed and in-progress cloud applications. This requires PaaS, in addition to supporting application hosting environment, to possess development infrastructure including programming environment, tools, configuration management, and so forth.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has several advantages to enterprises, the following are some of the benefits that were the reason for the adoption of cloud computing in your industries:
- Cost saving
- Increased competitiveness
- Flexibility/Scalability
- Guarantees for cloud services
- High level of data security
- Reliability
- Easily to maintain
- Facilitate communication to create innovation
- Green Environment Enhancement (environmentally friendly)
- Produce products at relatively affordable prices
Challenges in Adopting Cloud Computing for Businesses
On the other hand, there are some challenges facing enterprises on the use of cloud computing, even though, the cloud service providers are always coming up with the innovative ideas and techniques that will enhance the security and reliability of the data stored in the cloud. Among the challenges are:
- Lack of control capability
- The need for ICT specialists>/li>
- The Needs for Internet Connection
- Security Risk and Interruption of Service
- Regulatory compliance
- Latency
Even though with these challenges of adopting cloud computing that may arise for businesses during intial automation change over stage, the overall benefits for adopting the cloud technology in our businesses has outnumbered the challenges.
Don't forget to share the article on your social media handles by clicking the Share button so that others can also benefit!
 AbdulBasid Usman
AbdulBasid Usman

No comments:
Post a Comment